The osteochondrous process affects a spine or more at the same time.The lumbar and cervical vertebrae are the most affected by pathologies, as the most sensitive to the loads due to the anatomy of the human skeleton.
The consequences of vertebral osteochondrosis in the cervical region cause the most drawbacks and potential complications, because the neck is a zone rich in neuromusive highways, many of which directly feed the brain.
For this reason, clinical symptoms with cervical osteochondosis are much associated with the ischemia of brain areas.In addition, the nerve roots, which provide the sensitivity and motor activity of the hands and the shoulder belt, when the compression of the destroyed vertebrates can give a variety of symptomatic images.
Below, consider the general clinic of osteochondrosis of the cervical column.
Dizziness
Luries are also due to a violation of the blood flow to the organs of the inner ear, which ensures the balance of the body.NYSTAGM often joins dizzy - arbitrary fluctuations of eye students on the sides.
Lack of air
This feeling appears due to the irritation of the ends of the diaphragmatic nerve.It is a component of the cervical nervous beam and is involved in the regulation of breathing, its depth and its frequency.Patients complain about the inability to breathe in the chest.
In some cases, the symptom worsens with severe shortness of breath and suffocation.For the same reason, breathing stops at night and snoring.
The disadvantage of oxygen due to respiratory problems is ultimately the cause of the increase in fatigue, a decrease in concentration and memory problems.
Nausea
He is accompanied by Burning Air.Also due to blood circulation problems in certain areas of the brain and inner ear.Nausea is sometimes observed with indomitable vomiting caused by the movements of the head and body.The consequence of nausea and frequent vomiting is a decrease in appetite, weight loss, food insufficiency.
Vision problems
The "flies" in the eyes, a decrease in visual acuity, fog in front of the eyes - all the symptoms due to the ischemia of the brain area that is responsible for vision.
Patients with osteochondosis complain less vision, as the lack of blood supply of vertebral vessels is offset by the blood flow of the carbon arteries system.
Glasses and therapeutic gymnastics for eye muscles do not solve the problem, generally vision improves after the treatment of osteochondrosis.
An unstable pressure level is due to an alteration of blood flow in the oblong brain which is responsible for the functions of the vascular-motor center.
It occurs with brain arteries spasms due to the short -term stop of blood flow along the vertebral arteries.
From the state of loss of consciousness of the patient, you can quickly be removed by placing it so that the legs are slightly higher than the head - the blood flow to the brain allows a person to drive to life.
After a fainting attack, reversible problems with speech and movements, due to a brief stop on blood circulation, can be observed for a while.
Green symptoms
It is often the only sign indicating cervical osteochondrosis.They are expressed as perspiration, drought and a feeling of a bump in their throat, difficulties swallowing.Symptoms are associated with compression of the nervous plexus responsible for the innervation of the pharynx.These manifestations are necessary to differentiate from a similar clinic for inflammation or neoplasms.
The increase in body temperature for cervical osteochondosis is not the most typical symptom, it is rarely and locally observed: in the cervical and collar area, with a light redness of the skin.
The osteochondrosis clinic in the cervical column can, first of all, be various degrees of gravity, it depends on the stage of development of the pathology, also during the periods of exacerbations that they are brighter and, secondly, to form in certain syndromes.
Step I
The start of degenerative processes in the cartilage of vertebral discs.Symptoms are weak, sometimes it may not be observed at all.The first signs of osteochondrosis of the cervical column:
- Discomfort in the neck, arms, shoulders, sometimes turning into pain;
- headache;
- Easy restriction of the motor motor activity;
- quickly passing visual disorders;
- Reduce the sensitivity of the skin of the collar area.
Important: these symptoms become more pronounced when tilting the head.
As a rule, in the first stage of osteochondrosis in the cervical region, patients do not go to the doctor, believing that all symptoms are associated with fatigue, stress, age, lack of sleep.
Stadium II
At this stage, the vinental projection began, the narrow intervertebral cracks, the collagen fiber of the fiberisal ring of the disc is destroyed.There are notable painful symptoms of a punctual nature due to the compression of the nervous trunks, intensifying during the movements of the neck and the towers of the head.Here you can already suspect cervical osteochondosis, whose symptoms in the second step are as follows:
- Pain pronounced in the neck, sometimes with a crunch;
- The skin of the shoulders and hands almost completely loses sensitivity;
- The headaches are frequent, do not spend long;
- Visual business with "flies" in the eyes;
- sounds and noise in the ears;
- weakness of the muscles of the upper limbs;
- The clarity of the tendon reflexes is reduced;
- Shooting pain with dedication under the shoulder blades;
- The feeling of a bump in the throat, swallowing problems;
- Sleep disorders, generally insomnia.
Long maintenance of the head in a position leads to intense pain.At this stage of the development of the disease, patients are already coming to the doctor to get help.
Stadium III
The fibrous ring of the disc is destroyed, hernias are formed.In the third step, there is a deformation of the spine, displacement and dislocations of the vertebrae because of their low fixation.The symptoms are as follows:
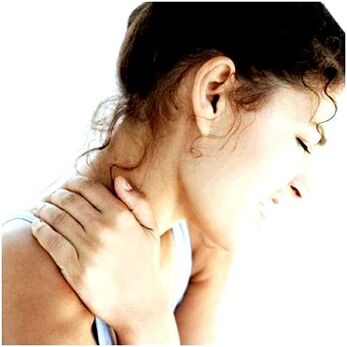
- Intensive and acute pain in the neck, collar area, heart zone;
- The sensitivity of the scalp at the back of the head, in the shoulder region, in the hands, until the complete absence of;
- hernia of the cervical column;
- paresis and paralysis of the upper limbs;
- Tendular reflexes are practically not observed.
It is a serious stage of the disease in which the patient is no longer able to support his head by himself.The ischemia of the spinal cord and the compression of the arteries of the spine lead to paralysis and paresis in other parts of the body and a stroke of the spine.
Non -specific and a large number of different symptoms that accompany osteochondrosis of the cervical column make diagnosis and subsequent treatment difficult, because some of them can be a completely different sign of diseases.Symptoms of cervical osteochondosis are formed in certain groups called syndromes.Their presence and severity can indicate a pathology in the cervical column with an updated location.
Clinical image of cervical column osteochondrosis - Signs, signs
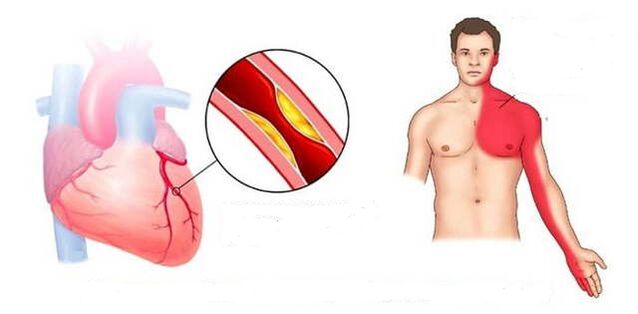
Osteochondrosis in the cervical region is a chronic and slowly progressive vertebral disease, in which the vertebrae, the joints and the intervertebral discs are affected and destroyed.The vertebrae from first to seventh, which belong to the cervical region, suffer.
As the disease progresses, the intervertebral discs lose their elasticity and their strength, relax, relax, their amortization properties aggravate.Such a deformation occurs due to the changes caused by power and exhaustion disorders.
These violations are one of the natural processes of aging the body, but various overloads, posture disorders, wounds, congenital anomalies of the spine and certain other causes cause early wear of cartilage and discs.
The pain can have a different location, they can be in the neck, in the occipital region, in the shoulder or the upper limb.Shoulder or hand pain appears when the spine of the innervates the upper limb is involved in the process.The pain in the occipital part of the head is caused by cramps in the neck muscles, which are attached to the occipital bone and the circulatory disorders of this area.
When symptoms occur:
- A decrease in sensitivity in the hand occurs when a spine is damaged, which contains sensitive nerves innervating the skin of the upper limb.
- The restriction of movements in the cervical column and crunching it during movements occur due to a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc, the appearance of bone growth on the bodies of the vertebrae and damage to the small joints between the cervical vertebrae.
- Lurin, altered coordination, weakness occurs in serious cases with high deterioration of blood supply to the occipital fraction of the brain, cerebellum and trunk.
- Language numbness, decrease in hearing and vision
All these symptoms are due to the involvement of the vertebral artery in the process, which takes place in its own channel located in the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae.Due to the development of cervical osteochondosis, the formation of fibrous tissue, the vertebrae of the vertebrae, the blood flow in these arteries worsens, which leads to a deterioration of the blood contribution to the occipital fraction of the brain and the brain.
Reasons
- Excessive physical activity in sports or heavy physical work;
- hereditary predisposition;
- neck hypothermia (walking in winter without scarf);
- Stress;
- work on the computer;
- obesity.
Some of the above causes cause osteochondrosis and other spine columns.
The degree of osteochondosis is determined by the clinical picture and the patient complaints.The concept of degree should not be confused with the stages of osteochondosis.The steps will be discussed below.

Considering and analyzing the procedure for the development of changes in the tissues of the vertebra, the doctors distinguished several stages of osteochondrosis in the cervical region:
- Preclinical phase.Cervical osteochondosis of the 1st degree is expressed by the displacement of the pulpose nucleus on the side and the beginning of the destruction of the fibrous ring.The pain in this period can be absent, a small lordosis and a difficulty turning or tilting the head are possible.
- Osteochondrosis in the 2nd degree cervical region is characterized by an increase in pathological destruction, the instability of the entire segment with subluxis, and pain appears, sometimes giving in the belt or the arm shoulder.The patient complains about distraction, a deterioration of memory and attention.
- 3rd degree osteochondrosis develops with a complete break in the fibrous ring.Neurological symptoms appear, sensitivity is disturbed.The pain in the third step becomes constant and greatly disturbs the patient.The mobility of the cervical segment worsens.
- Osteochondrosis of the 4 degree neck.The last step in the degenerative process.The intervertebral disc is completely replaced by connective tissue, all symptoms become more pronounced, a deterioration in the coordination of movements, is noted ataxia.
Depending on the location of pain, the following types of diseases are distinguished: radiculichemia, cervicobrachialgia, cervicanranalia and cervicalgia.
According to the method, of course, the disease is customary to divide into acute intervertebral osteochondosis, which appears for the first time and chronic, extending for years with constant remissions and exacerbations.
Which doctor treats cervical osteochondosis?
The variety of symptoms, often hidden under the mask of another disease, means that patients are a logical question - which doctor contact?When pain in the neck, shoulders and hands or occurrence of neurotic disorders, it is urgent to approach the neurologist or the vertebrologist.
And who to contact if there are no such specialists in the local clinic?In this case, the ticket must be reported to the therapist.The doctor will prescribe a treatment or send close specialization to the doctor.
Symptoms depending on the damaged vertebra
In addition, radicular syndromes can be distinguished, leading to one or the other of the sensitive and motors disorders.They differ according to the type of tight vertebra the vertebral root:
- C1: leads to numbness and altered sensitivity at the back of the head;
- C2: pain in the parietal region and the back of the head;
- C3: Weakening speech, sensitivity of language, pain and decrease in sensitivity on the side where the vertebral nerve is violated;
- C4: pain in the heart, left hypochondrium, in the shoulder, shoulder blade, respiratory disorders, decrease the tone of the neck muscles;
- C5: shoulder pain in the outdoor area;
- C6: the pain that gives in from the forearm to the thumb of the hand, as well as the neck on the Omoplade;
- C7: the pain on the rear surface of the shoulder, from the neck to the omoplade, gives the forearm to 2-4 fingers of the hand;
- C8: neck pain on the shoulder, from the forearm to the little finger.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
To make a diagnosis, instrumental questioning methods are used:
- X-ray examination of the spine department;
- myelography;
- Neurological study of sensitivity, reflexes.
Additional methods prescribed for differentiation and clarification of the diagnosis, the stage of pathology includes:
- Tomodensitometry of the vertebral column (CT);
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (JAMR);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
During the examination with the conduct of neurological tests, the doctor will assess the degree of mobility and neck pain, as well as alteration of blood flow in the vertebral artery.
Cervical osteochondosis requires not only the study of the vertebrae itself, but also nearby tissues, blood vessels, nerves.It is only then that we can judge the complete image of the pathological changes that have occurred due to a disease.
The diagnosis of cervical osteochondosis begins with a visual examination and a patient study.The neuropathologist is interested in the patient's living and working conditions, the presence of chronic diseases, nutrition and motor activity.
A preliminary diagnosis is confirmed by the conduct of instrumental research:
- X -Ray in two projections;
- MRI;
- Ct;
- UZDS (Duplex digitization).
An analysis of hormones is necessary for the fairer sex.Without this, the treatment of cervical osteochondosis in women does not start.
To exclude pathologies with such symptoms, a differential diagnosis is made with the appointment of additional consultations with a surgeon, a gynecologist, a cardiologist, an ophthalmologist and a tradition.
Complications of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical column is dangerous with its complications.With the unfavorable development of the disease, the compression of the vertebral artery can lead to a stroke, a persistent aggravation of hearing and vision.
Often, an intervertebral hernia, severe hypertension and numbness or cooling of the fingers join osteochondrosis.In women, neurological complications often develop - constant fatigue, lethargy, loss of performance, excessive resentment.
The non-compliance with the prescribed treatment, the prolonged avoidance of a doctor and the lack of therapy of osteochondrosis contributes to the progression of the disease and causes the development of complications, pathologies and new diseases, such as:
- hernia of intervertebral discs (hernia of the spine);
- projection;
- Cyphosis;
- radiculitis;
- Salt deposits in the intervertebral space;
- spinal cord;
- Reduction of members' muscle mass, muscular atrophy due to the supply of altered blood;
- Lower limbs paralysis.
Despite the fact that the 4th degree of osteochondrosis can occur without symptoms and pronounced pain, neglected osteochondosis is the most dangerous for the development of serious complications and can lead to the invalidity of the patient.
Medical physical education
The LFK for cervical osteochondosis should be carried out outside of acute exacerbation.The greatest efficiency of this technique during the recovery period.During the implementation of the complex, there should not be discomfort and pain!
| Exercise number 1 | Lying on your stomach, resting your hands on the ground, lifting your head and a torso, your back should be straight.Stay in this position for 1 to 2 minutes.Slowly flow to the ground.Repeat 2-3 times. |
| Exercise number 2 | Lying on your stomach, stretch your arms along the body, turn your head to the left, try touching the floor with your ear, then turn your head to the right.Repeat 6 to 7 times in each direction. |
| Exercise number 3 | In a sitting position, lean forward and try to touch your chest with your head, then exhale, lean back and throw your head.Repeat 10 to 15 times. |
| Exercise number 4 | When you sit, put your palms on your forehead, put pressure on your palms on your forehead and forehead on your palm.Continue this exercise for 30 seconds.Repeat 2-3 times. |
| Exercise number 5 | Slowly turn your head first in one direction, then in the other direction.10 rotations in each direction.Make sure there are no dizziness.When it appears, the exercise stops. |
Risk factors
The chances of increasing osteochondrosis if you have:
- Anomalies in the development of the spine;
- excess weight;
- long physical effort;
- Bad habits (smoking);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- The works, which implies the regular impact of vibrations on the spine (for example, with vehicle drivers);
- Long stress, excessive nervous tension;
- local hypothermia;
- previous injuries in the neck and nape;
- Autoimmune pathologies resulting in degeneration of cartilage.
Psychosomatic
The development of cervical osteochondosis indicates the inability to resist in a competent manner for problems.Sometimes people become so strong and confident in their abilities that their stability before adversity turns into rigidity and lack of flexibility.In this case, attempts to turn your head are accompanied by stiffness, convulsions and other unpleasant sensations.
In addition, osteochondrosis can develop in people who are afraid of problems and do not know how to deal with it.In this case, the protective reflex of the mammal is triggered and the head is literally attracted in the shoulders.This provision is considered to be unnatural, therefore, after a certain time, the muscles of the cervical region begin to hurt and deform.
Treatment
The treatment of cervical osteochondosis depends on the stage of the disease.If at the first stage, there is sufficiently conservative and wandering treatment, then in the second and third stages, the doctor's task is, first of all, to stop pain syndrome.Improved cases may require surgical treatment intended for decompression and stabilization of the vertebrae.
Drug
| Band | Description |
| NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) | Help eliminate swelling and pain.The most commonly used drug base is actor components such as sodium diclofenac. |
| Vasodilators | Contribute to improving blood circulation. |
| Sedatives, muscle relaxing | They are also prescribed to facilitate the general condition of the patient and reduce the doses of NSAIDs.Reliered at the same time the nerve nerve cramps and muscle cramps, help get a better therapeutic effect. |
At the end of the therapy, NSAIDs should be purchased for a home kit first, because pain in the neck can be returned periodically (with stress, on -cas, meteorological change).Before taking medication, see your doctor.
If a positive effect is not observed after a conservative treatment of a conservative treatment, the doctor may recommend the patient in fussy.
This procedure allows you to immobilize the assigned vertebral segment.
Its essence is to eliminate the intervertebral disc, the decompression of the nerve root, the installation of the implant or the creation of the physiological height of the disk space.
The operation has many side effects and contraindications.Thus, this can cause a vertebrogenic handicap.This is why surgery is carried out in extreme cases.
Massage with cervical osteochondosis allows you to obtain notable improvements.It is important that the procedure is carried out by a professional: incompetent movements in the field of the cervical column can worsen the situation.The movements must affect the collar area, the cervical region and part of the back.
Pay attention to the technique of carrying out exercises for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosasas for osteochondrosis implies the alternation of the following actions.
- Caressing.The masseur affects the surface layers of the skin, moving from the head to the upper third of the middle of the back.At the same time, the palms or the fingers work.
- Pressing.Deep layers of the skin located in the upper third of the back are exposed.In this case, the index and thumb of the hands through the neck are made to take the skin.The tissues adjacent to the vertebrae are not involved in this process.
- Trituration.It is made to warm the skin, increase blood flow in the neck area.The procedure must be carried out extremely carefully.It is forbidden to influence the thorny processes of the vertebrae.Sometimes the friction is replaced by circular lines or movements resembling sawing.
- Kneading.It affects deeply lies tissues, so it has a limited value.It can worsen pathology.
During the massage, the patient must lie on the belly, in extreme cases, sit down.
Prevention

For the prevention of the disease, it is recommended:
- For the health of the spine, it is important on which the pillow passes to sleep on a pillow and an orthopedic mattress;
- Take a hot shower every day for 10 minutes;
- Visit a bath or sauna (relieves cramps from the neck muscles);
- Avoid inclinations and acute turns of the head;
- Walking more on foot, making yoga and swimming;
- With the "seated" work, take five -minute breaks every hour (you have to walk during the breaks, inclination with a body and your head in different directions);
- Avoid increased load on the spine: classes with weights, jumps, race;
- Choose chairs and chairs supporting the spine;
- abandon dependencies, such as smoking, alcohol abuse;
- Drink at least one and a half liters of water per day.
Eating with cervical osteochondosis is often recommended (at least five times a day) and small portions.The preference must be given to cooked or cooked dishes.Salads must be seasoned with olive oil.